Amongst the willows lining the road just below where the tall poplar, birch, spruce and pine trees stand, there is a passage. A small party of hunters hopes it leads to a healthy mineral spring. But hunting in B.C.’s South Peace isn’t what it used to be. The hunters fear the mineral spring is gone: disappeared in the oil-and-gas rich area that saw one of its driest years on record in 2012.
There are no clear reasons why the springs, which are used by animals such as Canada’s iconic moose, are vanishing in the province’s northeast corner along the B.C.-Alberta border. These springs are known to hunters in the area as moose licks.
One hunter in the party stops to consider the disappearing mineral springs. “We hunted these licks since our childhood. My brothers and I would hunt them with our dad, and we travelled to them by foot over the years,” the hunter says. “There has been a change to how we access the trails to the licks; in some cases these changes have been made by the oil-and-gas companies. In many cases, the licks are gone when we do get to them.”
Resting at the northern tip of the Rocky Mountains, the South Peace is an embattled land where farming anchored the economy until a natural gas boom in recent decades changed things. The cultural centre of the region is Dawson Creek, B.C., a town of about 11,000 people that boasts the title “Mile Zero” of the Alaska Highway.
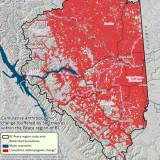
The area is situated 600 kilometres northwest of Edmonton, and about 1,200 kilometres northeast of Vancouver. The South Peace covers 32,000 square kilometres of land stretching north to Fort St. John, west to the Williston Reservoir, east to the Alberta-B.C. border, and south to the Pine Pass where the Rocky Mountains begin.
2012: a dry year
People hunt largely for subsistence in the South Peace, not to acquire trophies. This is a distinction proud hunters in the area will emphasize. Many South Peace hunters believe it’s their right to hunt for subsistence. Many hunters belong to families that have hunted for generations.

Métis elder Malcolm Supernault belongs to one such family. As a respected elder, former North East Métis Association president, and private security contractor, Supernault has hunted and trapped all his life. He enjoys talking about Canada’s icon, the moose – a hulking member of the ungulate family that can weigh up to 700 kg and measure more than 2 metres tall. Supernault is worried about the impact of consecutive droughts on moose that he says rely on mineral springs in summer for water.
“This year was a dry year,” Supernault says in a recent phone interview. “As a rule, moose licks are used in the summer. You’ll find those moose licks will dry up.” Supernault says human activity often pushes wildlife out of traditional mating areas. “Every cow moose has an area where they raise a calf, and unless they’re forced off, they will stay. It’s humans that have caused the most havoc. Industry is everywhere.”
It’s not all bad for moose licks though. Supernault says resource development often creates new areas where springs are able to bubble back to the surface as long as there’s enough moisture created from the ground below or air above. He explains not all moose licks are mineral springs; instead, many are swamps that dry up faster than mineral springs during droughts.
Supernault is cautious about placing blame on any one reason for the disappearing moose licks, but says he’s seen how resource activity affects water supplies. “Anytime you put equipment over a piece of ground, it impacts the moisture right away. Drilling as well, pretty soon the underground streams change. Now industry is starting to pay attention. Water is our lifeline,” Supernault says.
More natural gas than you can imagine
In April 2011, the Canadian National Energy Board and B.C. Ministry of Energy and Mines released a report entitled, “Ultimate Potential for Unconventional Natural Gas in Northeastern British Columbia’s Horn River Basin.” The report says there are 5.58 trillion cubic metres of natural gas deposits in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin – an area spanning from the B.C.-Northwest Territories border to southern Alberta.
With large new discoveries continuing to emerge like Apache Corp’s play in the Liard Basin, west of the Horn River, that number will likely end up being much higher.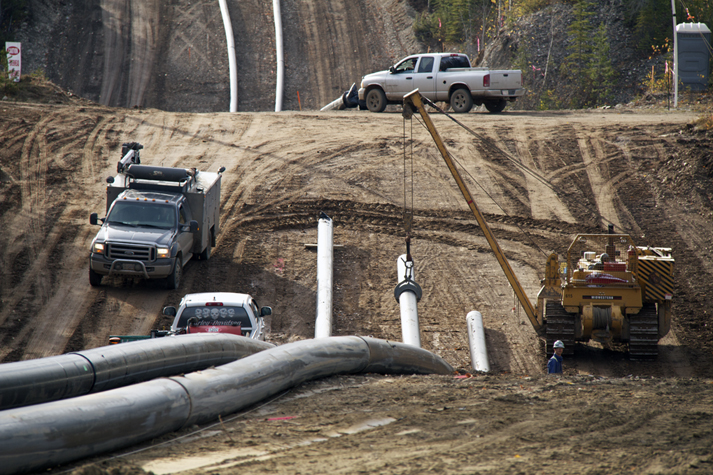
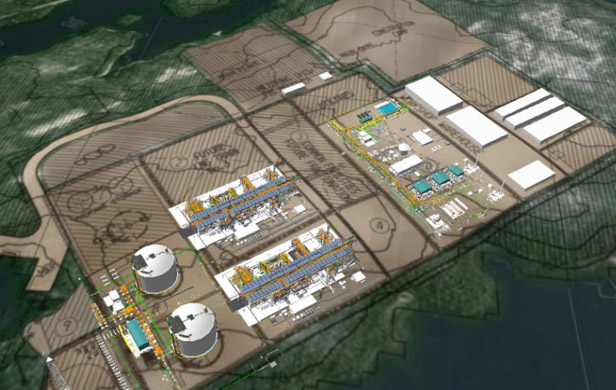
The report also says there are 3.09 trillion cubic metres of natural gas from this basin in Northeast B.C., with 2.21 trillion cubic metres of shale gas compared to .878 trillion cubic metres of conventional fields. This means there are many more shale gas deposits in B.C. requiring hydraulic fracturing, or fracking for short, to extract.
By comparison, Canada’s Lake Superior contains 1.21 trillion cubic metres of water, and is the third-largest freshwater lake in the world by volume, and the largest by surface area. Yet its water volume is only half the estimated volume of shale gas in Northeast B.C.
In the South Peace, where mineral springs are disappearing as severe droughts cause water supplies to vanish, the City of Dawson Creek saw its average water use spike to 9,464 cubic metres between August and September this year, whereas water use hovers around 5,678 cubic metres on average in other months.
This year the city and B.C. Oil and Gas Commission issued a water restriction in September on industrial use of water in the South Peace. In its 2011 provincial water use report, the B.C. Oil and Gas Commission indicates rivers where shale gas is extracted see an increase in water volume usage.
For instance, the Upper Petitot, East Kiskatinaw, and Kiwigana rivers see on average a .81 per cent use of annual water runoff compared to other rivers which fall far below this average. This may seem an insignificant amount of water, but when natural gas activity increases during summer months, these rivers’ annual runoff is much depleted by the time there’s a drought.
Drought response level 4
Outside of the regular problems associated with resource activity, such as loss of habitat for wildlife and pollution, fracking requires substantial amounts of water. In B.C., water-use permits are granted by municipalities, which supply much of the water the oil-and-gas industry in the area requires.
The B.C. Oil and Gas Commission, a regulatory agency, also grants short-term water permits (known as Section 8 permits) if companies apply to draw water from sources outside of municipal boundaries. These two institutions work together in times of drought by restricting the use of potable water by industry, as was the case this past summer.
For Dawson Creek Mayor Mike Bernier, it’s a balancing act because the oil-and-gas industry drives the local economy. In a recent phone interview, Bernier acknowledges severe droughts are changing the way city officials deal with water shortages. For instance, the municipality partnered with Shell Canada to build a water reclamation plant that uses waste water to feed natural gas fields.
The Kiskatinaw River, a tributary of the Peace River that branches off and travels southwest through resource-rich lands, is at its highest in spring when the snowpack melts. Bernier says the city is looking to build more reservoirs to store water collected when the city’s water source is at its peak.
“It has been quite something the last couple of years with four out of six as recorded drought years. This year was our driest year in recorded history,” Bernier says in the phone interview. “It’s always a balance with industry in the area so heavily dependent on water. We do work with different companies in the area and look for different ways to recycle. Companies are sensitive on issues around water shortages.”
This past summer, the city issued a Drought Response Level 4 advisory that required the city to obtain maximum reduction of water use as directed by the B.C. Drought Response Plan to avoid a loss of water supply. This cut off the oil-and-gas industry from both city and B.C. Oil and Gas Commission water-use permits. “It’s a last resort,” Bernier says. “We value our economy and jobs more than green lawns.”
Bernier explains city officials are working to further their understanding of the watershed. He says water issues are cyclical. The mayor compares 2012’s drought with 2010’s flooding that destroyed roads, homes, and entire hillsides all across Northeast B.C. “It’s been all over the map. This year, because of the drought, the river almost dried up to nothing,” Bernier says, adding there are times the Kiskatinaw River produces more water than the city needs. Now the municipality is looking at ways to increase the number of reservoirs in the area to ensure there’s always water in times of drought.
Water troubles further north
A five hour drive North from Dawson Creek, Fort Nelson First Nation is grappling with its own water challenges relating to shale gas development in the Horn River Basin. The nation’s new chief Sharleen Wildeman is quick to point out her members benefit from employment in the industry, but her community is concerned about 20 new long-term water licence applications on their territory currently before the Ministry of Forests, Lands and Natural Resource Operations.
“Fort Nelson First has worked with the natural gas industry and government to provide economic opportunities for our members and the entire province through responsible resource development. But our concerns regarding irresponsible, unsustainable water use have gone ignored,” the chief says during a delegation she led recently to Vancouver to raise these concerns.
These new licences mark a shift in water use for shale gas in both their long-term duration and in the enormous volumes of water they represent. For example, Encana is applying to draw up to 3 billion litres a year out of the Fort Nelson River for its nearby shale gas operations. Nexxen Corp.’s licence, the first and only application to be approved so far, is for five years, but under the current Provincial Water Act, these long-term licences can extend for up to 40 years. Fort Nelson First Nation recently won the right to challenge Nexxen’s licence at the Environmental Appeal Board.
Fort Nelson First Nation is calling on the provincial Liberal government to halt the issuance of these new licences until the community and general public have been properly consulted and a responsible long-term water management plan is in place. The nation’s leaders put forth a series of additional demands, such as gathering proper baseline data, adequate monitoring and enforcement measures and the ability to make certain culturally sensitive rivers off-limits to development.
Watch a timelapse animation of increasing water withdrawals for shale gas in Fort Nelson First Nation territory.
Water shortages are no coincidence
For groundwater expert Dr. Gilles Wendling, water shortages in areas of heavy natural gas extraction are no coincidence. Wendling is managing director and director of the technical and professional division of the B.C. Groundwater Association. He’s also president and founder of Global Aquifer Development Foundation, a Canadian charity that helps create groundwater management systems in developing nations.
“The problem is most of the cyclical perception is anecdotal. We are seeing low flows in rivers. We have to take notice of what people are reporting, especially First Nations people who have a close connection with the land,” Wendling says in a recent phone interview.
“Surface and groundwater are intimately connected. Water can travel deep into the subsurface, 1, 2, 3 kilometres is possible. What they’re doing with fracking may affect the groundwater at that depth. If you start reducing groundwater, it can result in a drop of the water at surface. It may shut down springs.”
Wendling said when fracking occurs, holes are often drilled deep below ground to allow for the injection of water to free up natural gas. This water dissipates, leaving conduits from the surface to the natural gas layer that rests sometimes 3 kilometres deep. As the natural gas is extracted, there’s a potential for the creation of high-pressure zones near the surface where shallow water is contained below lakes, rivers, swamps and springs.
This creates a vacuum between low pressure areas at the natural gas reservoir level and the high pressure areas at the more shallow depth where there’s groundwater. “You end up with a depressurization with a drop in the water table of the groundwater shallow aquifers,” Wendling says.
This means subsurface aquifers supporting above-surface water, such as mineral springs, are depleted as the water moves deeper to low-pressure zones created by the fracking.
A fracturing debate
The leading scientific journal Nature published an article last year asking the question, “Should Fracking Stop?”
In the article, Cornell University engineering professor Dr. Anthony Ingraffea and Penn State Geosciences professor Dr. Robert Halwarth argue against natural gas fracking. The academics point out most fracking today occurs to obtain natural gas from shale gas plays. It’s shale gas deposits requiring fracking that make up most of the fields in Northeast B.C.
“Fracking also extracts natural salts, heavy metals, hydrocarbons and radioactive materials from the shale, posing risks to ecosystems and public health when these return to the surface. This flowback is collected in open pits or large tanks until treated, recycled or disposed of,” the authors write in the article “Should Fracking Stop?” (September 15, 2011).
The professors outline water concerns as well, referring to a peer-reviewed study that “[found] about 75 per cent of wells sampled within 1 kilometre of gas drilling in the Marcellus shale in Pennsylvania were contaminated with methane from the deep shale formations.” As for drinking-water contamination, municipalities that handled waste from fracking operations have reported serious problems.
The article goes on to say pollution of water is also a problem. “[There] has been contamination of tributaries of the Ohio River with barium, strontium and bromides from municipal wastewater treatment plants receiving fracking wastes. This contamination apparently led to the formation of dangerous brominated hydrocarbons in municipal drinking-water supplies….”
Dr. Terry Engelder, who is a leading authority on the recent Marcellus gas shale play in the U.S., argues in the same Nature article that the benefits of burning natural gas far outweigh the negative effects of extraction using fracking methods. “Global warming is a serious issue that fracking-related gas production can help to alleviate. In a world in which productivity is closely linked to energy expenditure, fracking will be vital to global economic stability…,” Engelder writes.
Engelder admits one of the biggest causes for concern in fracking is water use. “Millions of gallons of water are required to stimulate a well…. Obtaining adequate water for industrial fracking in dry regions such as the Middle East and western China is a local concern, but is no reason for a global moratorium,” he writes.
According to the New York Times article, “Studies Say Natural Gas Has Its Own Environmental Problems” (April 11, 2011) by Tom Zeller Jr., the arguments for natural gas as clean energy are disputed. “The problem, the studies suggest, is that planet-warming methane, the chief component of natural gas, is escaping into the atmosphere in far larger quantities than previously thought, with as much as 7.9 percent of it puffing out from shale gas wells, intentionally vented or flared, or seeping from loose pipe fittings along gas distribution lines,” Zeller writes.
Many are gone
Ahead of the hunters, the forest opens up to reveal a healthy moose lick. There is a thick pattern of wildlife tracks in the muddy clay where water bubbles to the surface.  Moose licks are shallow by nature, and are protected from humans by the fact that if a person walks into one, they end up sinking into mud up to their knees. And it isn’t the kind of mud that’s easy to walk out of. Many licks are littered with the boots of hunters who wandered too far into a spring.
Moose licks are shallow by nature, and are protected from humans by the fact that if a person walks into one, they end up sinking into mud up to their knees. And it isn’t the kind of mud that’s easy to walk out of. Many licks are littered with the boots of hunters who wandered too far into a spring.
The hunters make their way to the top of a perch overlooking the mineral spring. It stretches out before them. It’s one of the largest in the region according to a hunter, who smiles when he looks out over the lick. He’s happy this one remains. Many moose licks are gone.
As effects of global warming increase, it’s not just places such as the Middle East and China that experience the side effects. Already regions across the globe are experiencing unprecedented changes to weather patterns. This includes the consecutive summer droughts in places like the South Peace where the mineral springs are drying up.
With files from Damien Gillis.







 Moose licks are shallow by nature, and are protected from humans by the fact that if a person walks into one, they end up sinking into mud up to their knees. And it isn’t the kind of mud that’s easy to walk out of. Many licks are littered with the boots of hunters who wandered too far into a spring.
Moose licks are shallow by nature, and are protected from humans by the fact that if a person walks into one, they end up sinking into mud up to their knees. And it isn’t the kind of mud that’s easy to walk out of. Many licks are littered with the boots of hunters who wandered too far into a spring.